Blockchain
The Intro
Every agreement/arrangement in this world is based on trust! This trust created and destroyed empires (colonial, imperial, capitalist, socialist, communal, and so on), and it also sparked the need for next generation technology on how things functioned in this digital age.
Trust: firm belief in the reliability, truth, ability, or strength of someone or something.
Historically, third parties such as insurance, escrow, government law and order, and so on have fulfilled this trust. However, this can result in additional costs, delayed processing, loss of privacy, and risk from untrustworthy third parties.
Through technology, blockchain aims to address these drawbacks. Instead of relying on trusted third parties, blockchain platforms use specialized software running on a network of decentralized computers to verify transactions.
Blockchain: A peer-to-peer distributed ledger that is cryptographically secure, append only and update by consensus.
The basic unit of blockchain network is a node. A node consists of one or more computers that verify, store, and broadcast transactions to ensure that transactions are synchronized across the network.
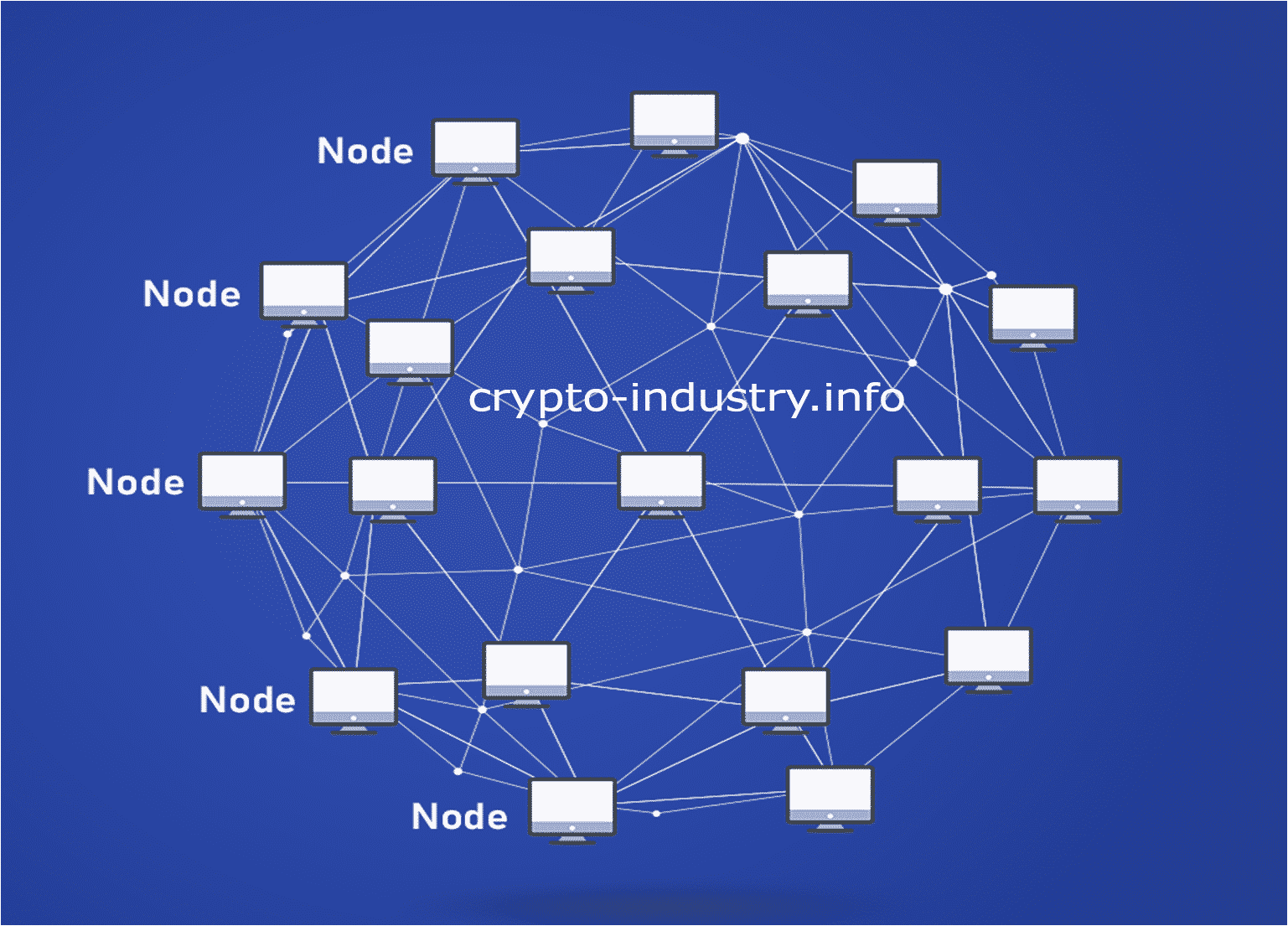
A Peer-To-Peer
When you put above picture and the definition of blockchain into context you can realize the behavior of peer-to-peer where no single node or group controls other nodes. This fundamentally solves the drawback of untrustworthy third parties.
Distributed Ledger
A ledger is the record of all transaction, in case of blockchain you have a distributed network of nodes maintaining the copy of entire ledger and collaborated to maintain its sanctity by agreeing on every action. This solves the drawback of single point of failure and single source of authority.
Cryptographically secure
Cryptography is an encryption scheme with guarantees against tampering by providing incontrovertible proof of data integrity by employing encryption, encoding and higher order mathematics.
Append only
Every block in the ledger has a unique fingerprint that is tamper proof, this is what makes append-only transactions possible. By design you cannot update or delete a transactions from the ledger, any updates needed has to be a new block that is agreed upon by the network. This ensure immutability
Update by consensus
As we discussed above any addition to the ledger will be done upon achieving certain level of consensus from the nodes on the network. Understanding how nodes reach these consensus is an important topic.
The consensus algorithm is based on honest nodes to come to an agreement on the state of a blockchain ledger and reject attempts of invalid entries. This is the paradigm shift from third party trust to consensus based trust.
Cheers and Happy Building 🤘
